What genetic conditions do we test for?
Eugene’s carrier tests only include serious and actionable conditions.
1. Serious genetic conditions
Conditions that impact a child’s life expectancy or development and have limited treatment options.
2. Results are actionable
The knowledge of being a carrier can open up reproductive options, including using IVF to avoid passing on the condition.
3. Relevant to everyone
With screening options ranging from 3 to over 780+ genes, our tests are relevant for people of all ethnicities & backgrounds.
What our tests cover
Carrier screening
Core
conditions
Couples
conditions
Comprehensive
conditions
Health Impact Categories
These charts show the distribution of genetic conditions across 7 health impact categories in our core, couples, and comprehensive carrier screening panels. The chart widths are proportional to the total number of conditions in each panel.
Each condition is categorised based on the primary body systems and functions it affects. The categories help understand the breadth of health impacts covered by genetic screening.
Hover over segments to see detailed information about each category.
Carrier screening at a glance

Screening breadth across tests
Screening breadth across tests
- All three options (Core, Couples, Comprehensive) screen for serious, actionable genetic conditions recommended by major professional bodies.
- The Core test covers CFTR, SMN1 and FMR1 and will detect 20% of at-risk couples, while the Comprehensive panel which includes more than 780 genes can detect ~90% of at-risk couples.
- The Couples test expands to hundreds (620+ genes) is only available for heterosexual couples and can detect ~80% of at-risk couples. It is important to note that common conditions such as Alpha Thalassaemia, Autosomal forms of non-syndromic hearing loss and Gaucher disease are not currently included in this panel.
Who the test is for
Who the test is for
- Core: Designed for an individual (female at birth) under Medicare‐eligible circumstances.
- Couples: Targeted at heterosexual couples (both partners) under Medicare eligibility.
- Comprehensive: Suitable for individuals, heterosexual couples, same-sex couples, or donors — offering maximum flexibility.
Report type & reproductive risk output
Report type & reproductive risk output
- All tests provide a reproductive risk assessment (i.e., risk of having an affected child) where relevant.
- Individual carrier results are included for all tests, but the Core and Couples test restricts to female only (in low risk scenarios); Comprehensive screening provides individual reporting across all genes.
- Please note, males are not screened for variations in X-linked genes. If a family history is reported please reach out to our genetic counselling team to discuss specific details counsellors@eugenelabs.com
Medicare rebate / out-of-pocket
Medicare rebate / out-of-pocket
- Core and Couples tests have Medicare rebate eligibility, reducing or eliminating out-of-pocket costs for eligible patients.
- The Comprehensive test is fully self-funded (no rebate), reflecting the broader gene panel.
- Please note that MBS item 73451 can only be claimed once in a person's life. Patients can check eligibility through Medicare claims history.
- If patients are not eligible for funded testing they will be contacted by the Eugene support team.
Turnaround time and logistics
Turnaround time and logistics
- All tests include genetic counselling support and standard logistics for sample collection and processing.
- The Core and Comprehensive tests aim for a quicker turnaround (around 4 weeks) while the Couples panel lists a somewhat longer timeframe (6-8 weeks), reflecting the additional complexity.
There are two types of conditions on Eugene’s carrier tests:
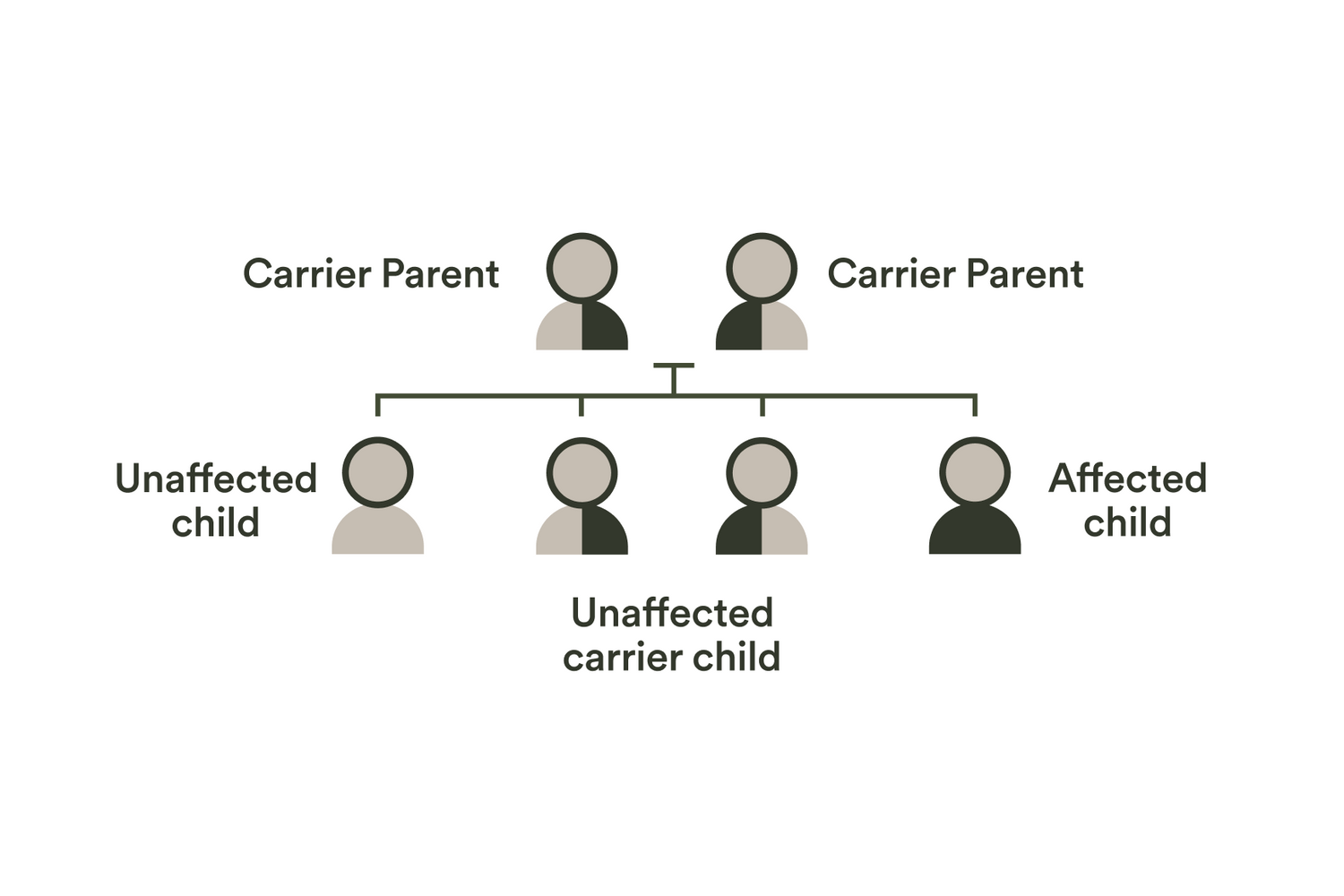
1. Recessive conditions
Recessive conditions cover the majority of conditions that are on the test. Carriers of recessive conditions are completely healthy and show no signs of the condition. However, if both parents are carriers of the same condition, there’s a one in four chance that their children would have the condition.
A couple of important things to note are that most people are carriers of one or more genetic conditions; And most children born with a recessive condition showed no family history of it.
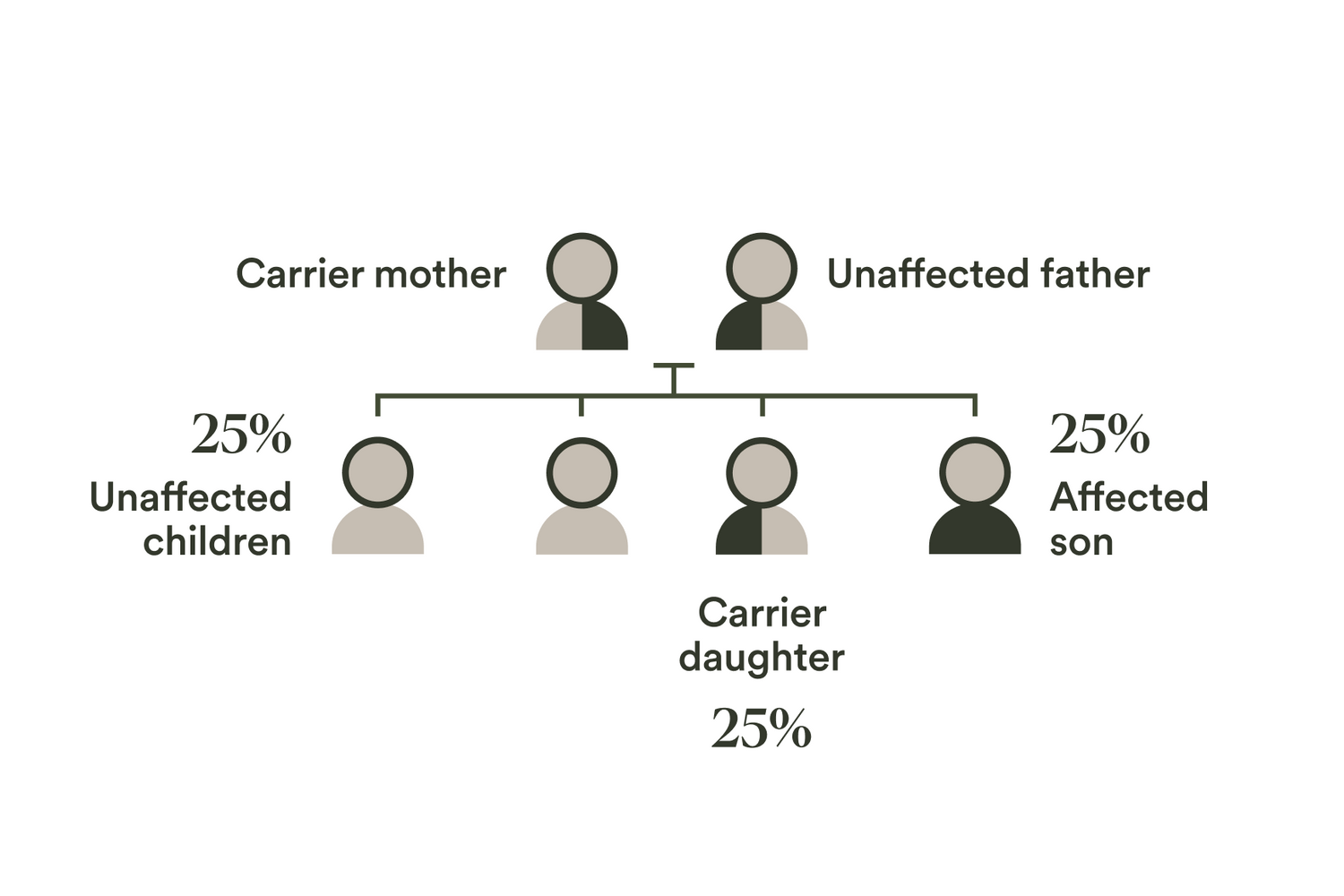
2. X-linked conditions
For x-linked conditions the sex of the parent who passes on the variant influences the risk for the children. They are generally passed on from carrier mothers and more commonly affect boys.
If the mum is a healthy carrier and they have a son, there is a 50% chance that the child could be affected by the condition. If they have a daughter, there is a a 50% chance that they will be a healthy carrier — like her mum. At Eugene only females are screened for x-linked conditions.
Compare genetic tests
Explore genetic testing options tailored to your needs.
| What's included | |||
| Total genes screened |
|
|
|
| Who is this test for? |
|
|
|
| Reproductive risk |
|
|
|
| Individual carrier result |
|
|
|
| Medicare rebate |
|
|
|
| Genetic counselling support |
|
|
|
| Express return shipping |
|
|
|
| Results turnaround time |
|
|
|

